External piles, also known as external hemorrhoids, are a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This comprehensive guide explores the appearance, symptoms, causes, and treatment options for external hemorrhoids, supported by visual references and medical insights.
What Are External Piles?
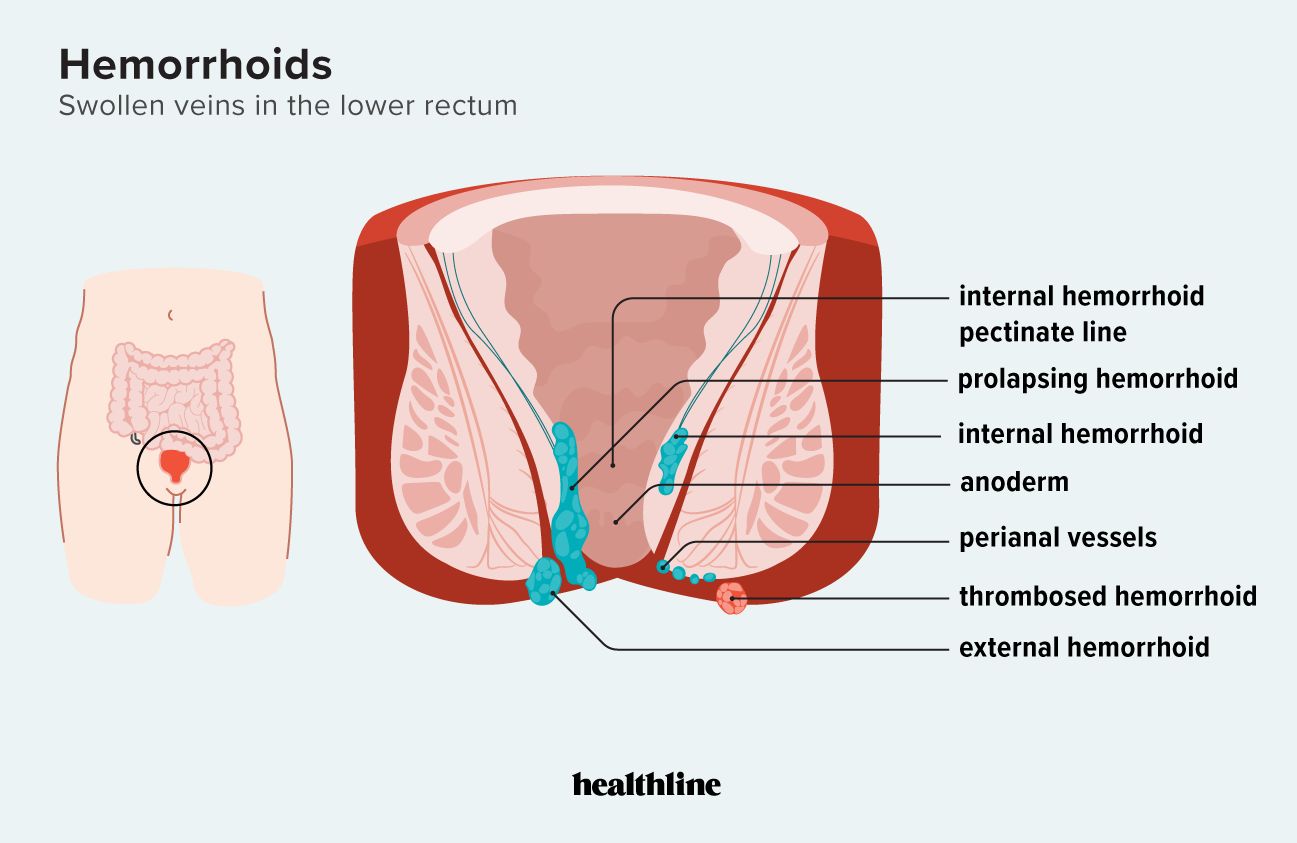
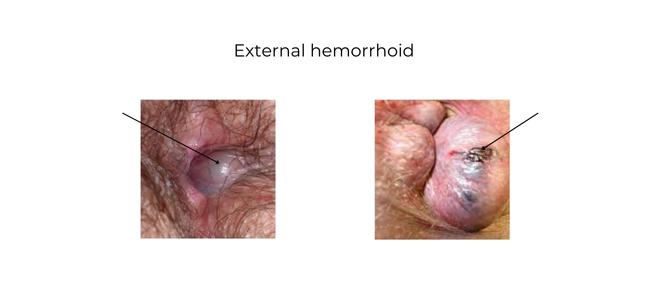
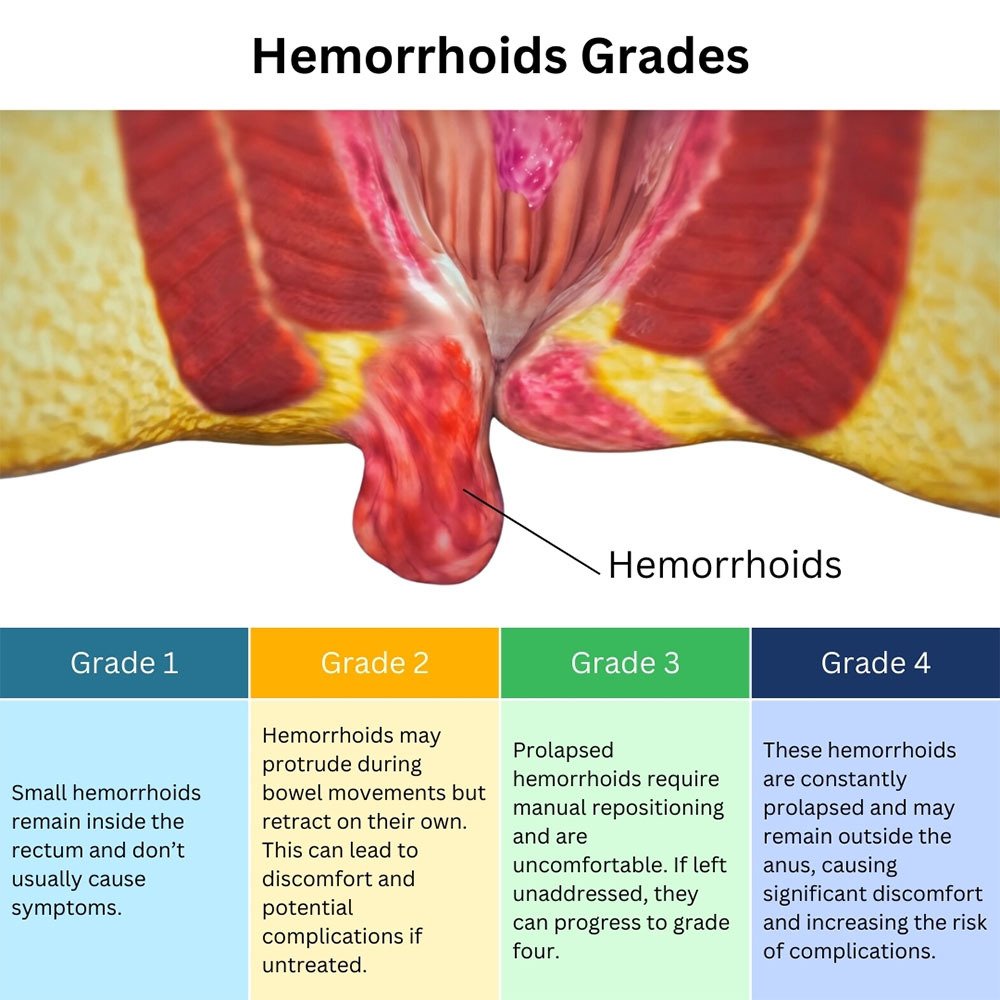
External piles are swollen veins located under the skin around the anus. Unlike internal hemorrhoids, which occur inside the rectum, external hemorrhoids are visible and often painful. They may appear as lumps or bulges and can cause significant discomfort during daily activities.
External Hemorrhoid Pictures & Appearance
- Typically appear as soft, bluish or purplish lumps near the anal opening
- May be tender to the touch or feel firm if thrombosed (clotted)
- Can vary in size from a small bump to a larger protrusion
- In some cases, skin tags may remain after healing
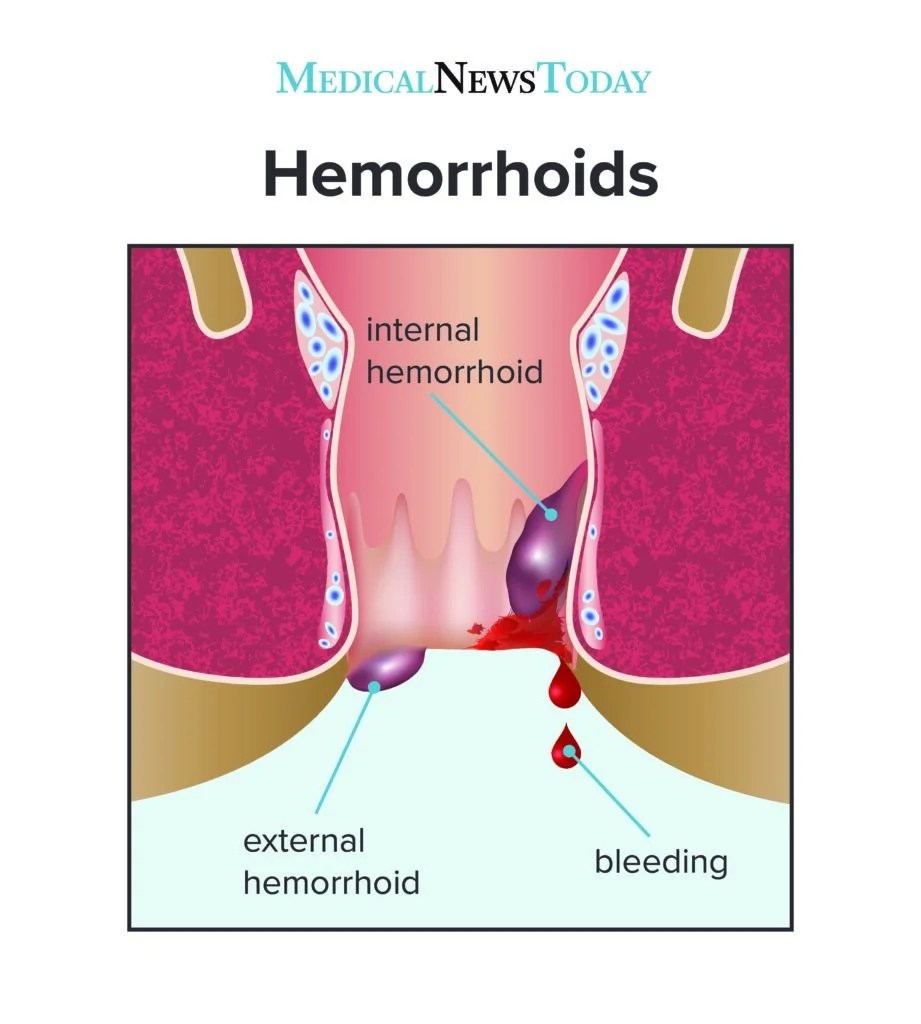
For visual references, you can explore Healthline’s hemorrhoid overview.
Common Symptoms of External Hemorrhoids
The symptoms of external piles can range from mild irritation to severe pain, depending on the severity and presence of complications like thrombosis.
Typical Symptoms Include:
- Pain or discomfort during bowel movements
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- Swelling or lumps near the anal opening
- Bright red blood on toilet paper or stool
- Difficulty sitting due to tenderness
Thrombosed external hemorrhoids may cause intense pain and appear darker due to blood clots beneath the skin.
Causes and Risk Factors
External hemorrhoids develop when pressure increases in the lower rectum, causing veins to swell and protrude. Several lifestyle and physiological factors contribute to this condition.
Leading Causes of External Piles:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Prolonged sitting, especially on the toilet
- Heavy lifting or physical exertion
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Obesity and low-fiber diets
- Aging and weakened anal tissues
Genetics and certain habits, such as frequent anal intercourse or overuse of laxatives, may also increase the risk.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
External hemorrhoids are typically diagnosed through a physical examination. A healthcare provider may visually inspect the anal area and perform a digital rectal exam to rule out internal hemorrhoids or other conditions.
In cases of bleeding or persistent symptoms, further tests like anoscopy or colonoscopy may be recommended to exclude colorectal cancer or anal fissures.
External Pile Treatment Options
Treatment for external hemorrhoids depends on the severity of symptoms and whether complications like thrombosis are present. Most cases resolve with conservative care, but medical procedures may be necessary for persistent or painful hemorrhoids.
Home Remedies and Conservative Care
- Warm sitz baths for 15–20 minutes several times daily
- Over-the-counter creams with hydrocortisone or lidocaine
- Witch hazel pads to reduce inflammation
- Ice packs to relieve swelling
- High-fiber diet and increased water intake
- Stool softeners to prevent straining
These methods often provide relief within a few days to a week.
Medical and Surgical Treatments
- Thrombectomy: Removal of clotted blood from a thrombosed hemorrhoid under local anesthesia
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical removal of the entire hemorrhoid, typically for severe or recurrent cases
- Laser or cautery procedures: Used to shrink hemorrhoidal tissue
- Prescription medications: Topical nifedipine or nitroglycerin may be used in some cases
Surgical options are generally reserved for large, painful, or persistent hemorrhoids that do not respond to conservative treatment.
Prevention Tips
Preventing external piles involves maintaining healthy bowel habits and reducing pressure on the rectal veins.
Key Prevention Strategies:
- Eat a fiber-rich diet (25–30 grams daily)
- Stay hydrated with 6–8 glasses of water per day
- Avoid prolonged sitting or straining on the toilet
- Exercise regularly to promote bowel function
- Respond promptly to the urge to defecate
- Avoid heavy lifting and excessive use of laxatives
Final Thoughts
External hemorrhoids are a manageable condition with a wide range of treatment options. Early intervention and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent recurrence. If you experience persistent pain, bleeding, or swelling, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and care.